AI chatbots have rapidly evolved from simple, rules-based responders to sophisticated virtual assistants capable of natural, human-like conversations. In the realm of UI/UX design, they’re reshaping the way users interact with websites, apps, and services. Whether you're a UX designer, product manager, or developer, understanding how to design intuitive, accessible, and delightful AI chatbot experiences is critical.
In this guide, we’ll explore how AI chatbots work, when and why to use them, UX principles to follow, and real-world chatbot design examples to spark your creativity.
While focusing your AI chatbot design, also try our free design and prototyping tool to quickly visualize and fully test your design ideas.
AI chatbots are virtual assistants built into websites or apps to help users get answers quickly and easily. While traditional chatbots follow fixed scripts and mostly pull from FAQs or tutorials, AI chatbots are much smarter.
They use technologies like natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to understand what users are asking, pick up on context, and improve their responses over time.
In UX design, AI chatbots serve as onboarding guides, support agents, product navigators, or even friendly brand voices—enhancing the overall user journey.
In today’s AI-driven era, their speed and intelligence create more seamless experiences, but well-crafted UI/UX design remains key to making those interactions intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable.

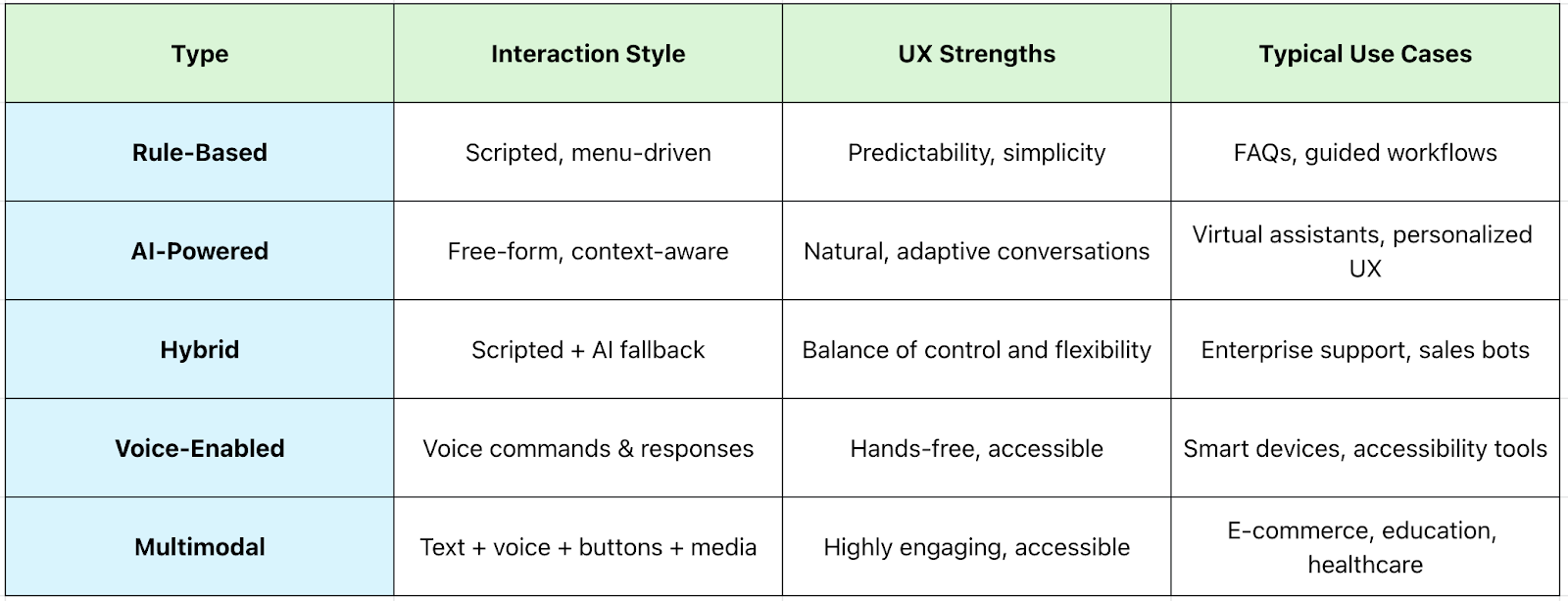
Understanding the various types of AI chatbots is essential for UX designers and product teams aiming to create effective conversational interfaces. Each type differs not only in technological complexity but also in its interaction style, user expectations, and suitable use cases.
Selecting the right chatbot type ensures that the design aligns with user needs and business goals.
These chatbots operate on predefined scripts and decision trees. They follow a linear path, responding to specific keywords or menu selections without any understanding of context or intent beyond programmed rules.
UX Implications: Rule-based bots are straightforward to design and predictable for users, making them ideal for simple tasks like answering FAQs or guiding users through fixed workflows (e.g., booking appointments). However, they can frustrate users if the conversation deviates from expected paths, as they lack flexibility.
Best Use Cases: Customer support for common queries, structured data collection, onboarding tutorials.
Powered by natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, these chatbots can interpret user intent, understand context, and handle more complex, dynamic conversations. They are capable of learning from interactions to improve over time.
(Tools like the free AI chat by paragraph-generator.com are great examples of how these systems enhance communication through intelligent conversation flows. )
UX Implications: This type offers a more natural conversational experience, adapting responses to user input and handling variations in language. However, they require careful design to manage ambiguity, provide fallback options, and maintain user trust.
Best Use Cases: Virtual assistants, personalized recommendations, complex support queries.
Hybrid chatbots combine the strengths of rule-based and AI-powered models. They primarily follow scripted flows but use AI to handle exceptions, ambiguities, or escalate conversations to human agents.
UX Implications: Hybrids offer a balance of control and flexibility, delivering consistent experiences while reducing dead-ends in conversations. Designers must carefully plan when and how AI elements intervene to avoid jarring transitions.
Best Use Cases: Enterprise support systems, sales assistants, and any scenario requiring fallback to human support.
These chatbots process and respond to voice commands and are integrated into smart devices or apps. They require speech recognition and voice synthesis technologies.
UX Implications: Designing for voice involves different considerations, such as handling ambient noise, managing turn-taking, and providing audible feedback. Accessibility and privacy concerns also play a critical role.
Best Use Cases: Hands-free interactions, smart home devices, accessibility tools.

Multimodal chatbots combine multiple input/output formats, such as text, voice, buttons, images, and even video. This versatility enhances engagement and accessibility by allowing users to interact in the mode they prefer.
UX Implications: Multimodal designs demand thoughtful orchestration of different interaction channels, ensuring consistency and smooth transitions. They can improve usability, especially for complex tasks or diverse user groups.
Best Use Cases: E-commerce assistants, educational platforms, healthcare apps.
Summary Table: Types of AI Chatbots
At the UX layer, AI chatbots work through conversational interfaces. Behind the scenes, their architecture typically includes:
Designers must ensure that this complex process feels seamless, intuitive, and friction-free for the user.
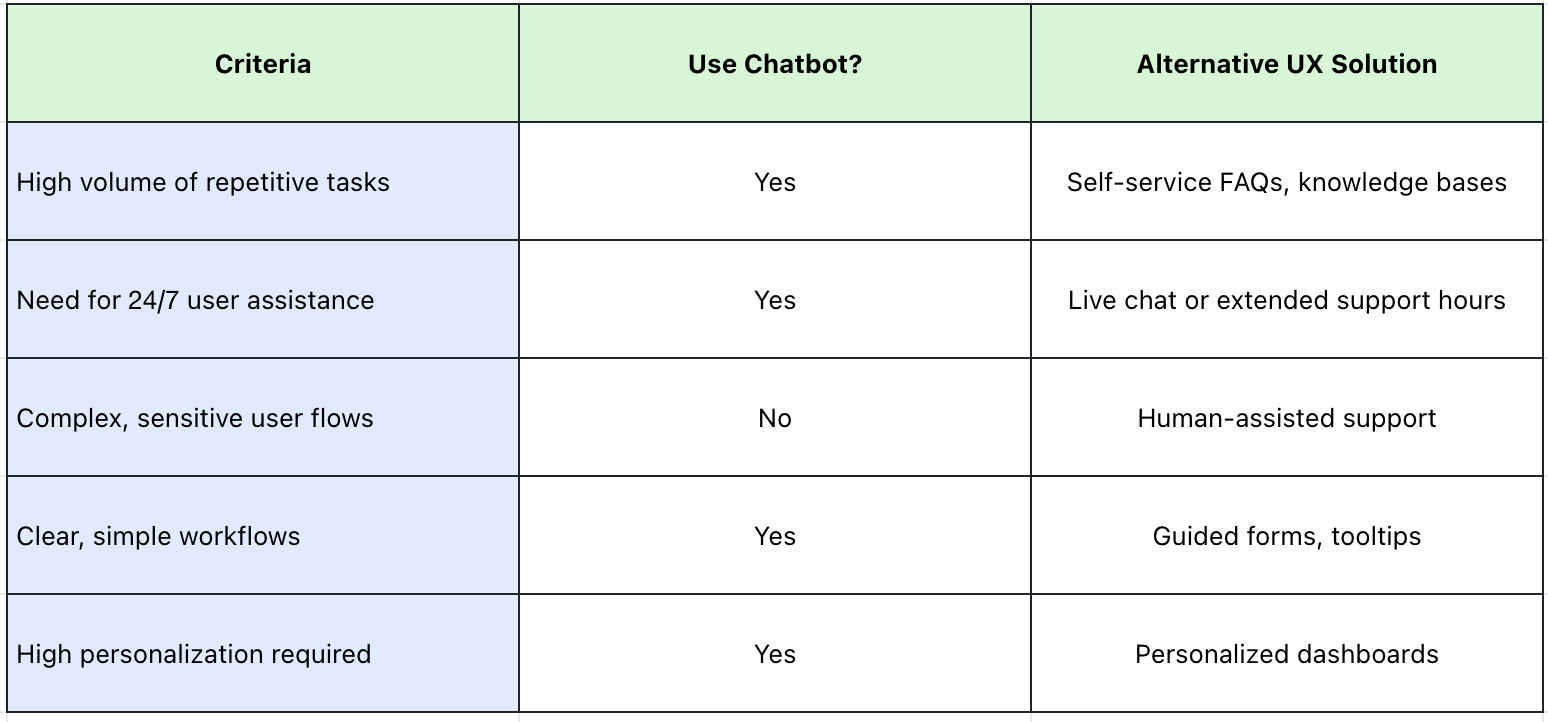
Integrating AI chatbots into your digital products isn’t just a trendy add-on—it’s a strategic UX decision that can profoundly impact how users engage, complete tasks, and perceive your brand. However, knowing why and when to deploy an AI chatbot is critical to ensure it adds genuine value rather than becoming a source of friction or frustration.
1.Enhance User Convenience and Speed
AI chatbots provide immediate, around-the-clock assistance, reducing wait times and making it easier for users to get help or complete tasks quickly. This immediacy can dramatically improve satisfaction and lower abandonment rates.
2.Simplify Complex User Flows
Many digital experiences require multi-step processes (e.g., onboarding, troubleshooting, purchases). Chatbots can break down these processes into natural conversational steps, making them less intimidating and more manageable.
3.Personalize Interactions at Scale
By leveraging user data and behavior, AI chatbots can deliver personalized recommendations, reminders, or content that fits individual needs—creating a more engaging and relevant experience.
4.Reduce Support Costs and Workload
Chatbots handle repetitive queries and common issues autonomously, freeing human agents to focus on complex problems. This increases efficiency while maintaining user satisfaction.
5.Facilitate Accessibility and Inclusivity
Voice-enabled and multimodal chatbots provide alternative interaction methods, supporting users with disabilities or different preferences, thus broadening your product’s reach.
6.Drive Engagement and Retention
Proactive chatbots that initiate conversations or provide timely tips can keep users engaged and encourage deeper exploration of features, improving retention metrics.
1.During User Onboarding and Education
New users often feel overwhelmed. A chatbot that offers interactive tutorials, answers FAQs, or guides users through key features can reduce drop-off and increase product adoption.
2.For Customer Support and Troubleshooting
If users frequently ask the same questions or encounter common issues, chatbots can provide instant support, reducing frustration and support ticket volume.
3.In Transactional Processes
Booking appointments, making purchases, or filling forms are prime candidates for chatbot assistance—breaking down steps and preventing errors through real-time guidance.
4.When Personalization is Critical
Chatbots that tailor product recommendations or content based on user preferences increase relevance and conversion rates.
5.To Enable 24/7 Assistance
For global or high-traffic products, providing support around the clock through AI chatbots improves user experience and brand reliability.
Complex, High-Stakes Tasks: Scenarios requiring precise or sensitive user input (e.g., legal, financial decisions) may not be suited for chatbots due to risk of misunderstanding or errors.
When Users Prefer Human Interaction: Certain contexts (e.g., crisis support) demand empathy and nuanced communication best handled by humans.
If Chatbot Technology is Not Mature Enough: Deploying chatbots without sufficient NLP capabilities or fallback options can lead to frustration and brand damage.
Decision Framework: Is a Chatbot Right for Your UX?
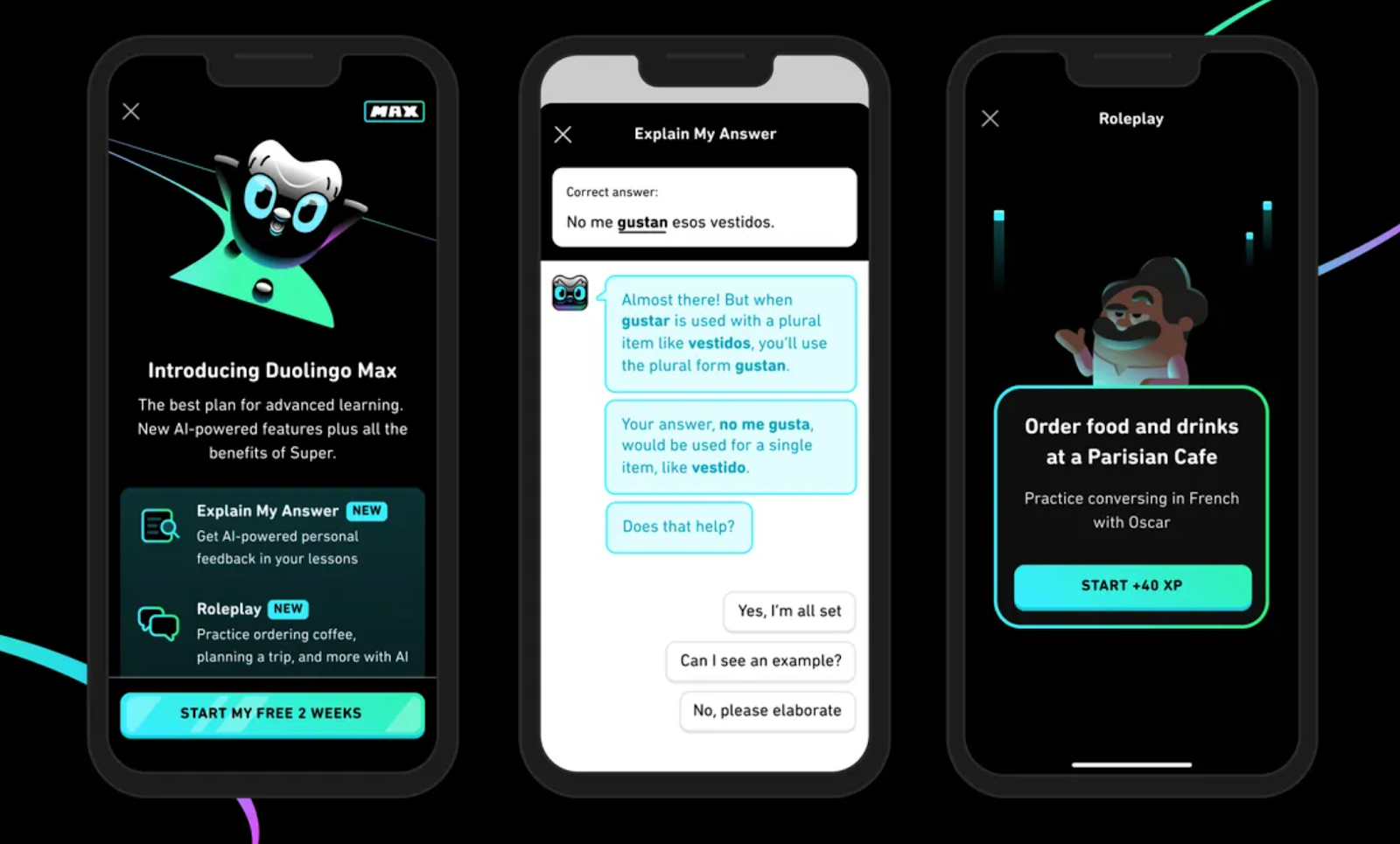
Duolingo’s chatbot acts as a conversational partner for language learners, simulating real-life dialogues to practice vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation.
UX Highlights:
Gamified Interaction: The chatbot incorporates points, streaks, and challenges, turning learning into an engaging game that motivates users to return daily.
Contextual Feedback: Immediate, constructive corrections help users learn without frustration.
Adaptive Difficulty: The bot adjusts conversation complexity based on user skill level, creating a personalized learning path.
Mascot-Driven Branding: The friendly Duolingo owl mascot is woven throughout the experience, reinforcing the brand’s approachable and playful personality.
What you can learn : Combining educational content with gamification and strong brand elements can create a more engaging, personalized, and memorable user experience that keeps users coming back.
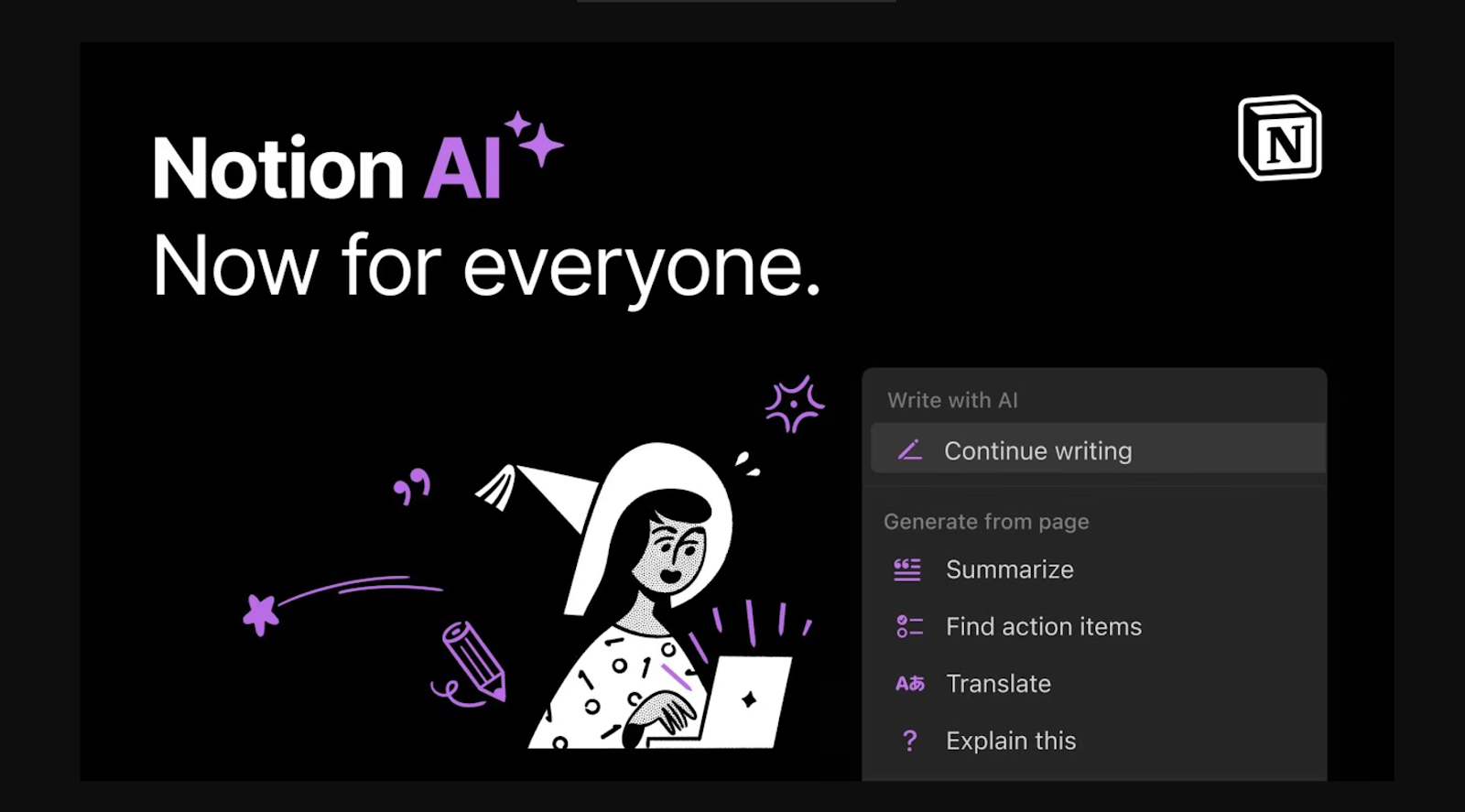
Embedded directly within Notion’s productivity platform, this AI assistant helps with writing, brainstorming, summarizing, and task management. Notably, it also enables voice-based interactions, letting users complete tasks using simple voice prompts.
UX Highlights:
Seamless Integration: The AI tools are integrated into the existing interface without interrupting the workflow.
On-Demand Assistance: Users can summon the AI assistant as needed, giving control over when and how they receive help.
Context Awareness: Suggestions and responses consider the current document context for relevance.
What you can learn: Integrating AI features directly into the user’s daily workflow—rather than separating them into a standalone tool—boosts efficiency, reduces friction, and makes the experience feel intuitive and natural
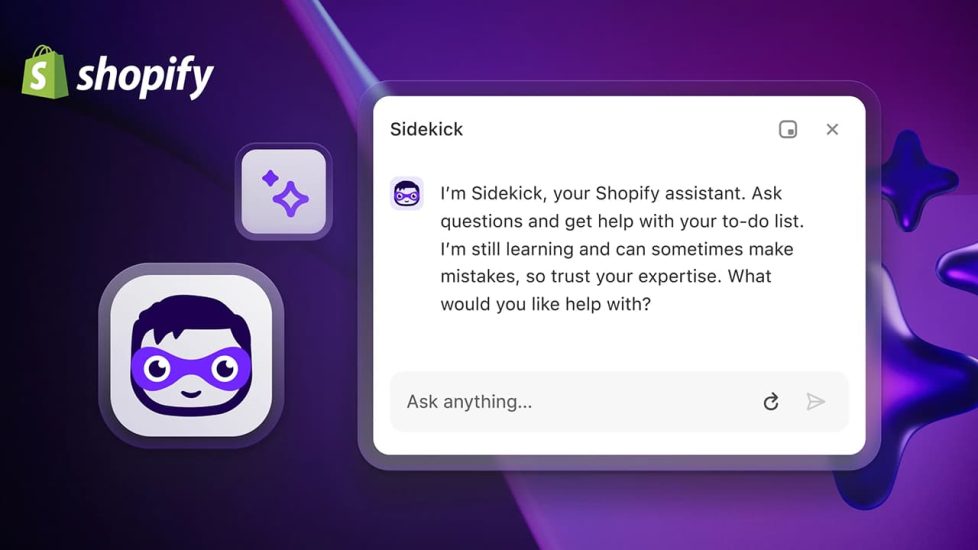
Sidekick is a virtual marketing assistant that simplifies advertising, social media posting, and sales reporting for Shopify merchants.
UX Highlights:
Conversational Marketing: Uses natural language messages and questions to make complex marketing tasks accessible to non-experts.
Actionable Suggestions: Proactively recommends next steps based on data insights.
Cross-Platform Messaging: Interacts via SMS and Facebook Messenger, meeting users where they are.
What you can learn: Meeting users in their preferred communication channels increases adoption and engagement.
4.Google AI chatbot – AI Chatbot for Knowledge and Exploration

Google Gemini is an advanced AI chatbot designed to assist users with information discovery, content generation, and task support. Powered by Google’s large language models and integrated with Search, Bard provides up-to-date, contextually rich responses across a wide range of topics.
UX Highlights:
Conversational Exploration: Bard encourages natural, back-and-forth interactions, making complex searches feel like chatting with a knowledgeable guide.
Real-Time Information: Unlike static chatbots, Bard pulls in fresh content from the web, ensuring users get timely and relevant answers.
Multimodal Input: Users can ask questions using text or voice, and even include images to receive context-aware insights.
Editable Responses: Users can refine or adjust the response tone, length, or detail level with a single click—offering a more tailored experience.
Google Ecosystem Integration: Bard connects with tools like Gmail, Docs, Maps, and YouTube, helping users take action directly within the conversation.
What You Can Learn:
When designing AI chatbots for UX, prioritize real-time relevance, personalization, and flexibility. Allowing users to guide and refine responses empowers them and improves overall satisfaction.
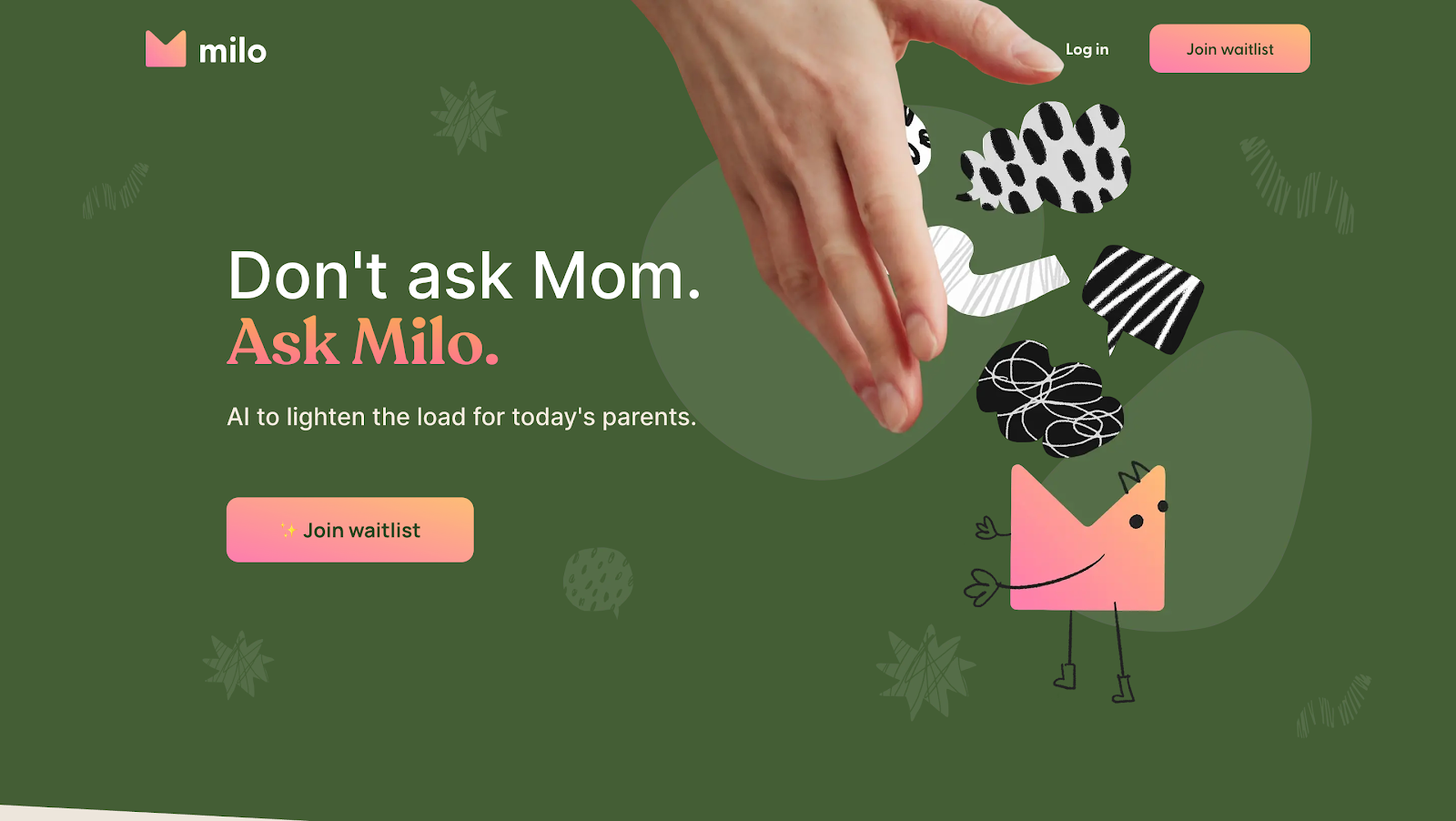
Milo is an AI-powered chatbot designed to guide and support parents through the ups and downs of raising children. It offers tailored advice, helpful resources, and a listening ear—whenever parents need it most.
UX Highlights:
Empathetic Communication: Uses warm, calming language that feels supportive and non-judgmental—especially important during stressful moments.
Personalized Guidance: Adapts tips and suggestions based on the child’s age, developmental stage, and the parent’s specific concerns.
Built-in Resources: Seamlessly integrates helpful articles, parenting communities, and tools within the chat, so users don’t have to search elsewhere.
What You Can Learn:
Designing with emotional intelligence—through tone, personalization, and thoughtful content—builds deep user trust and fosters long-term engagement.
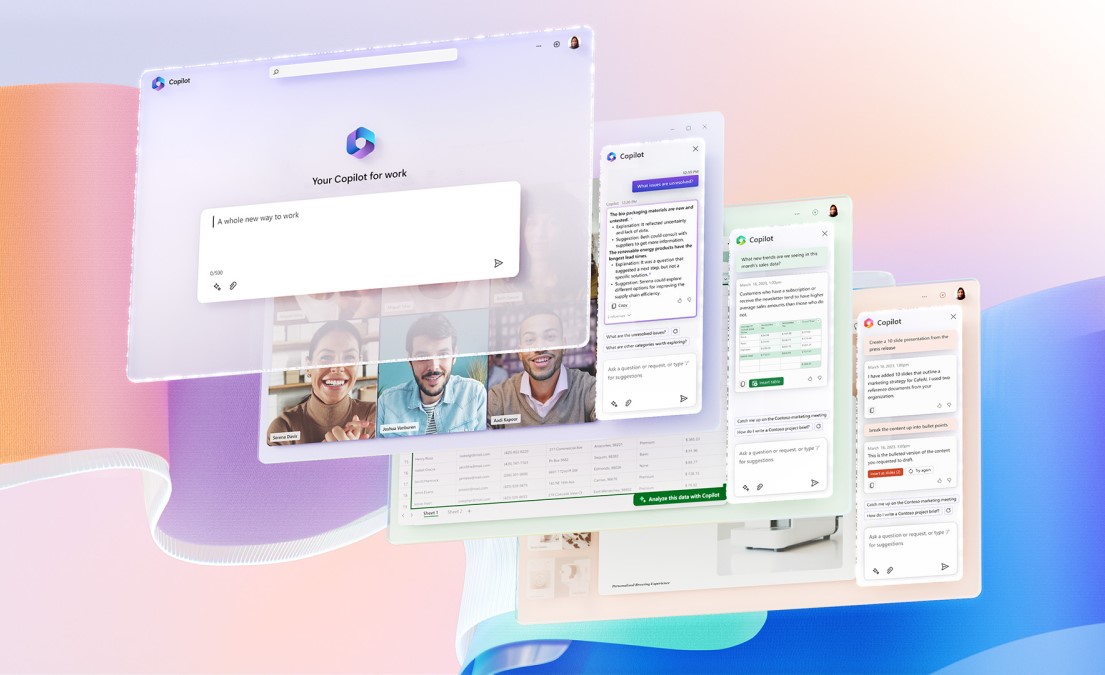
Integrated into tools like Microsoft 365 (Word, Excel, Teams, etc.), Microsoft Copilot is an AI chatbot that helps users write, analyze data, summarize meetings, and automate routine tasks—all within familiar work environments.
UX Highlights:
Native Integration: Copilot is embedded within Microsoft’s core apps, allowing users to access AI features without switching contexts.
Multi-Modal Support: Users can interact via text or voice and receive formatted outputs like charts, documents, or tables—reducing the time spent on manual work.
Contextual Intelligence: The chatbot understands the current file or conversation and offers relevant assistance tailored to what the user is doing.
Enterprise-Ready UX: Designed with privacy, compliance, and accessibility in mind, it balances power and usability for both individuals and large organizations.
What You Can Learn:
Deep integration with daily workflows, combined with contextual intelligence and enterprise-grade design, makes AI assistants truly useful and scalable across teams.
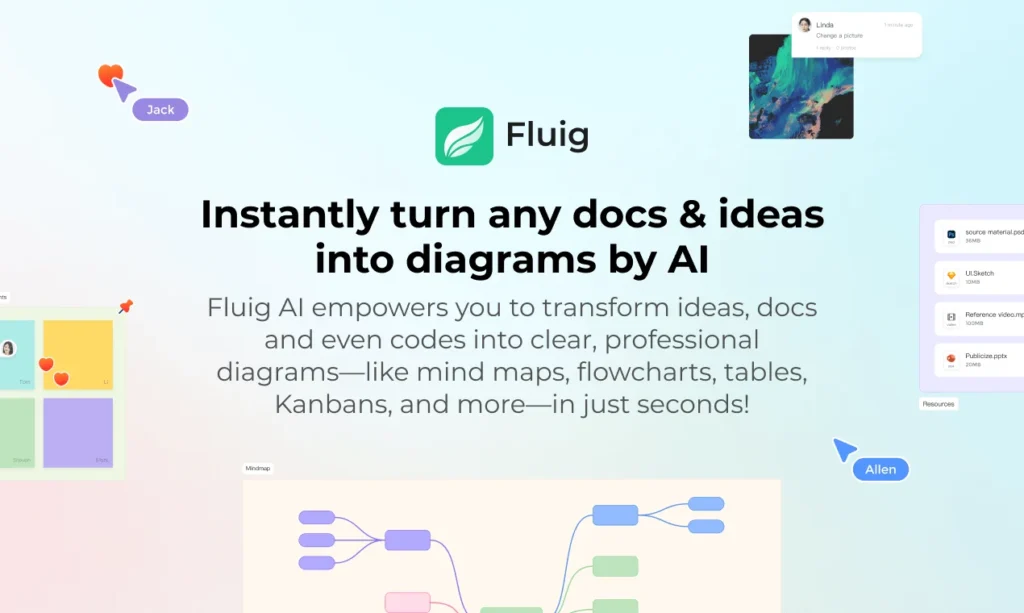
Fluig’s AI chatbot is deeply embedded into its AI-native diagramming platform, helping users brainstorm ideas, generate diagrams (like mind maps, flowcharts, kanban boards, and more), and collaborate in real-time. It acts not just as a support bot but as a thinking partner.
UX Highlights:
Interactive Visual Output: Instead of just giving text answers, the chatbot generates editable visual diagrams directly within the workspace—turning user input into instant output.
Multi-Format Flexibility: Whether you type ideas, upload files, or speak prompts, the chatbot interprets your input and creates structured visualizations accordingly.
Real-Time Collaboration: Teammates can interact with both the bot and each other within shared canvases, maintaining a smooth flow of work.
Agent Customization: Users can train their own assistant to fit specific workflows, improving the relevance and intelligence of responses over time.
What You Can Learn:
Going beyond text and offering actionable, visual, and collaborative AI responses creates a more immersive and productive user experience.
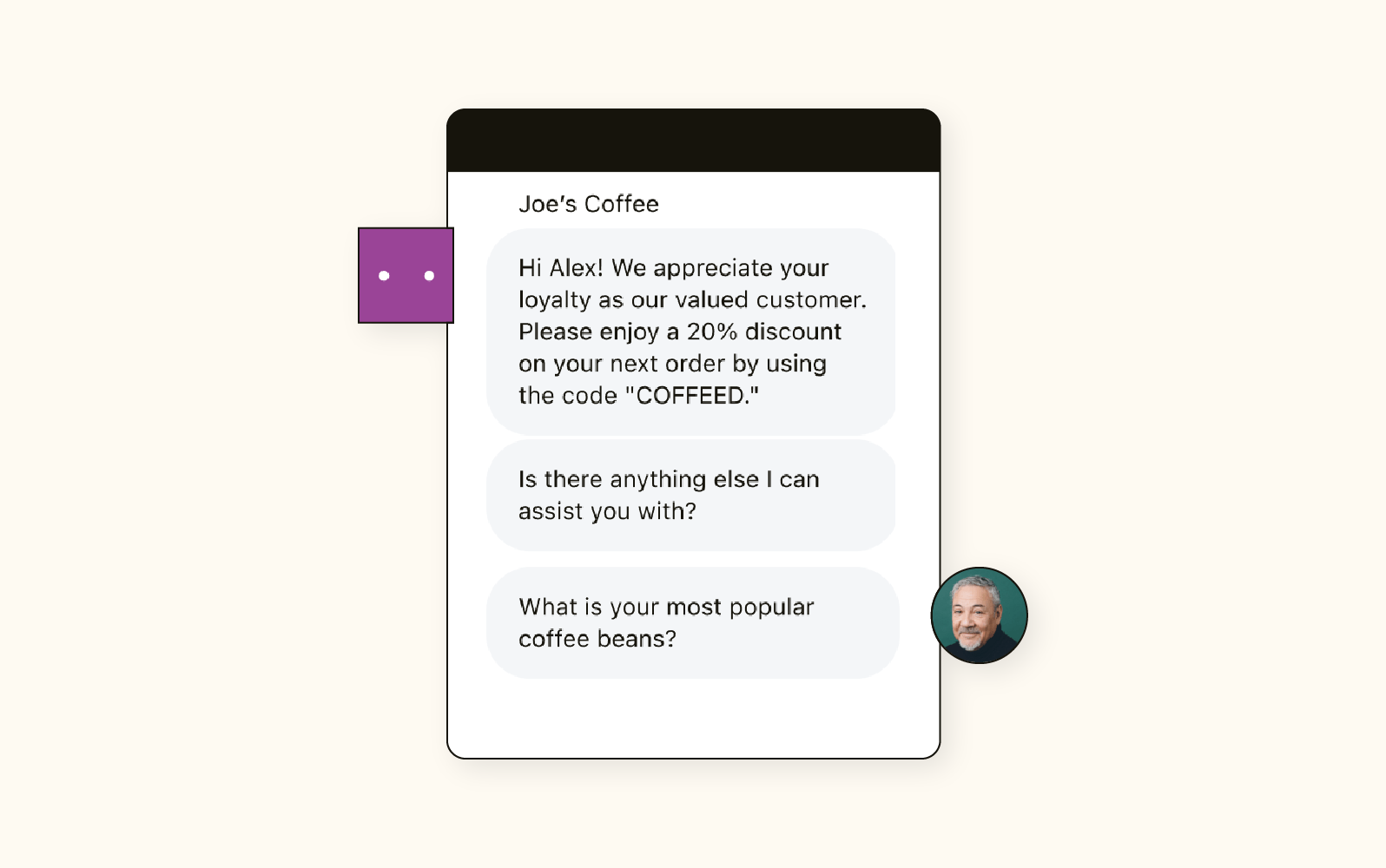
Zendesk’s AI chatbot is designed to streamline customer support by automatically handling common questions, guiding users through solutions, and escalating complex issues to human agents when needed.
UX Highlights:
Seamless Handoff: When the bot can’t resolve an issue, it smoothly transitions users to a live agent without forcing them to repeat information.
Smart Suggestions: The chatbot pulls answers from your help center and knowledge base, offering relevant, accurate solutions instantly.
Multilingual Support: It recognizes and responds in multiple languages, making it accessible to global users.
Ticket Deflection: By solving simple queries up front, it reduces support workload and shortens response times.
What You Can Learn:
A well-designed AI chatbot not only solves problems faster but also enhances the overall support experience by balancing automation with human empathy.

SnapTravel’s AI chatbot helps users find and book hotel deals directly through chat platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and SMS, offering a simple, conversational alternative to traditional travel booking sites.
UX Highlights:
Conversational Booking: Users interact with the bot like texting a travel agent—no need to browse or fill out forms.
Personalized Deals: The chatbot tailors hotel recommendations based on preferences, location, budget, and past behavior.
Instant Notifications: It provides real-time updates on booking confirmations, price drops, and travel reminders.
Cross-Platform Convenience: Accessible through multiple messaging apps, meeting users where they already are.
What You Can Learn:
Delivering a complete service (like travel booking) through a familiar chat interface removes friction and boosts conversion, especially when paired with personalized and timely responses.

Woebot is an AI-powered mental health chatbot designed to provide conversational support using principles from cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). It helps users manage stress, anxiety, and mood through daily check-ins and evidence-based strategies.
UX Highlights:
Empathetic Interaction: Uses a warm, human-like tone that feels caring and non-judgmental—essential for sensitive mental health topics.
Daily Check-ins: Encourages regular self-reflection through short, manageable conversations, helping build emotional awareness over time.
Evidence-Based Techniques: Integrates CBT exercises like reframing thoughts or journaling into chat, making therapeutic techniques more approachable.
Non-Intrusive Design: The chatbot keeps sessions brief and user-led, reducing cognitive load and respecting the user’s emotional state.
What You Can Learn:
A supportive tone, consistency, and user control are crucial when designing AI chatbots for emotional or sensitive use cases. Trust grows when users feel heard—without feeling overwhelmed.
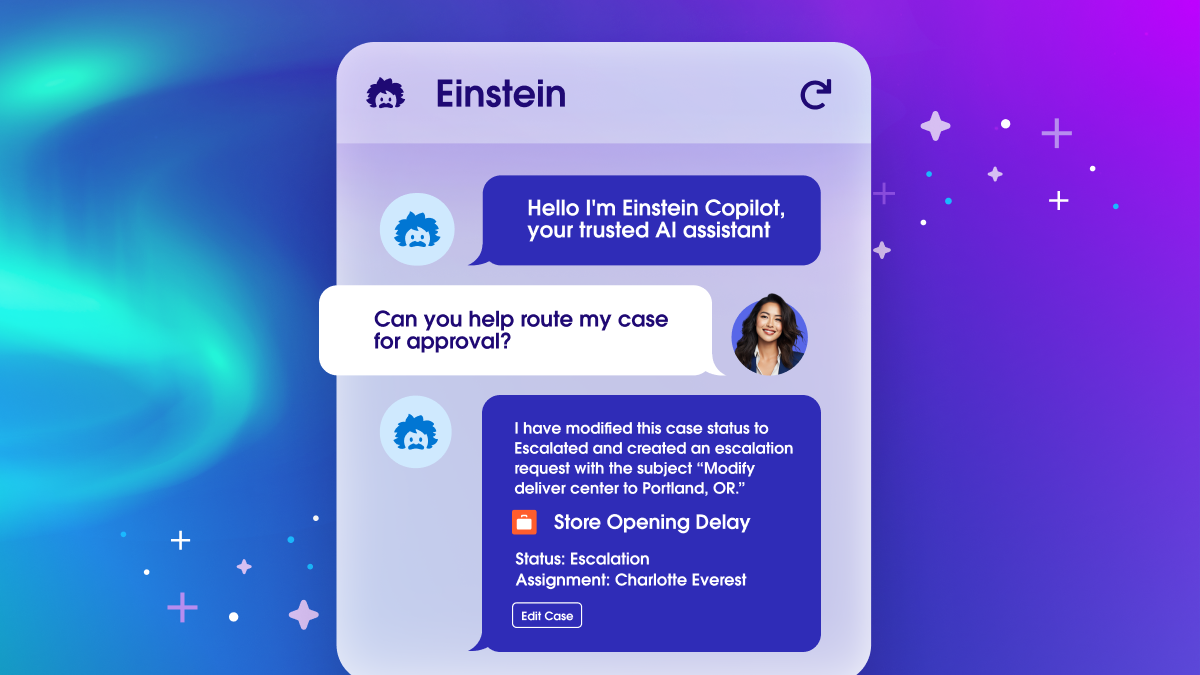
Einstein Copilot is Salesforce’s generative AI chatbot, built directly into the Salesforce ecosystem. It helps users across sales, service, marketing, and commerce by automating tasks, providing insights, and offering real-time assistance within the workflow.
UX Highlights:
Context-Rich Guidance: The chatbot understands CRM data in context, offering highly relevant suggestions, next steps, and summaries tailored to each user’s role.
Embedded Experience: It lives within the familiar Salesforce interface, so users don’t have to switch tools—reducing friction and boosting adoption.
Proactive Support: Instead of waiting for queries, Einstein Copilot can anticipate user needs (e.g., flagging risks or surfacing opportunities) and suggest actions in real time.
Natural Language Interface: Users can interact with it conversationally, making complex CRM actions more accessible—especially for non-technical users.
What You Can Learn:
Integrating AI into complex enterprise workflows works best when the assistant understands user context, anticipates intent, and stays within the tools people already use. This creates a more seamless, productive UX.

Landbot enables businesses to build conversational chatbots without writing code. It’s often used in lead generation, customer support, and onboarding across websites, WhatsApp, and Messenger.
UX Highlights:
Visual Builder: Its drag-and-drop interface lets teams design conversation flows easily, making chatbot creation approachable for non-developers.
Multi-Channel Support: Chatbots built with Landbot can be deployed across web, mobile, and messaging apps, ensuring a consistent experience.
Conversational UI: The interface mimics real conversations with rich media (buttons, carousels, images), guiding users intuitively.
AI Integration: Landbot can be powered by GPT-based models, combining structured logic with intelligent, human-like responses.
What You Can Learn:
Giving non-technical teams tools to build and deploy personalized chatbot flows quickly leads to faster iteration and more user-friendly conversational experiences.
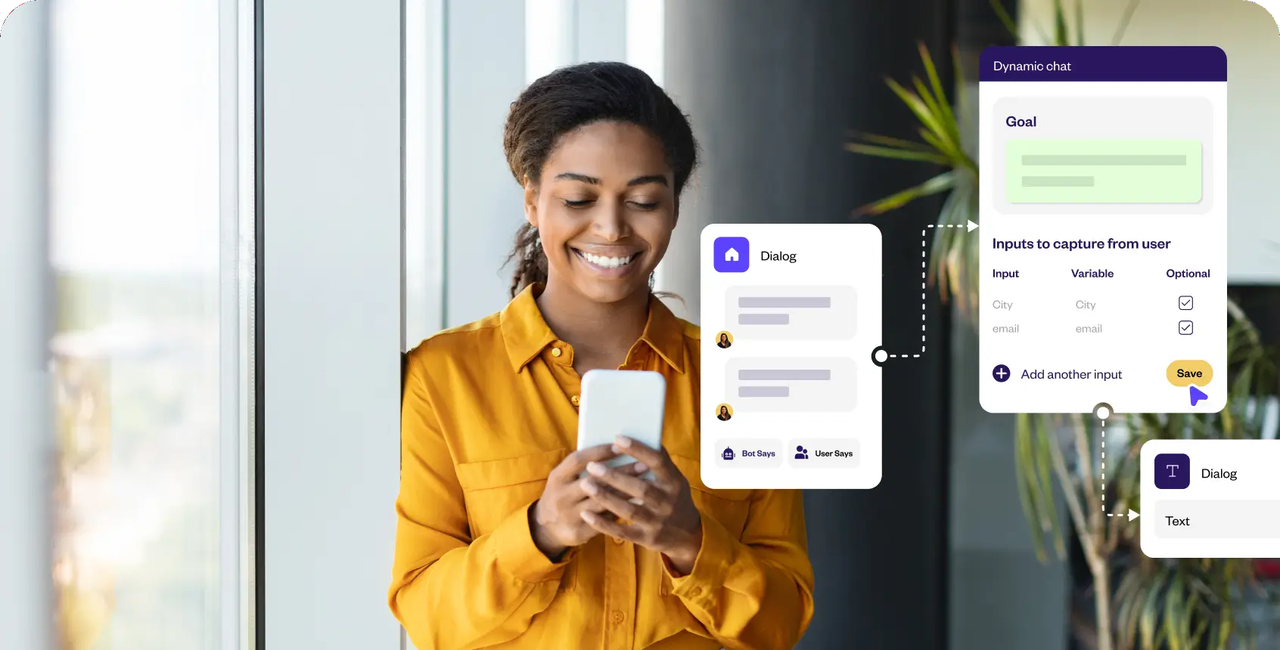
WhatsApp AI chatbots leverage the popular messaging app to deliver customer support, sales, and engagement through familiar, easy-to-use chat interfaces. Brands use these bots to interact with users where they already communicate daily.
UX Highlights:
Familiar Environment: Users engage with chatbots within the WhatsApp app, reducing friction since no new app or platform is needed.
Rich Media Support: Bots can send text, images, videos, documents, and interactive buttons to make conversations dynamic and helpful.
Instant, Real-Time Responses: Customers get fast answers to inquiries, improving satisfaction and reducing wait times.
End-to-End Encryption: Privacy and security are maintained, building user trust in sensitive interactions.
What You Can Learn:
Delivering AI chatbots on widely used messaging platforms increases reach and user comfort, making conversational experiences feel natural and accessible without additional learning curves.

IBM Watson Assistant is a powerful AI chatbot platform designed for enterprises to build and deploy intelligent virtual assistants across websites, apps, messaging channels, and call centers.
UX Highlights:
Robust Natural Language Understanding: Watson Assistant can understand complex queries, manage context, and handle multi-turn conversations smoothly.
Customizable and Scalable: Businesses can tailor the chatbot to specific industries and integrate with existing enterprise systems for seamless workflows.
Omnichannel Deployment: Supports deployment on web, mobile, messaging apps, and voice assistants, ensuring consistent user experiences across channels.
Analytics and Insights: Provides detailed conversation analytics to help improve chatbot performance and user satisfaction continuously.
Enterprise Security: Built with high standards for privacy, compliance, and data security, crucial for sensitive business environments.
What You Can Learn:
For complex, enterprise-grade chatbot needs, prioritizing deep language understanding, customization, and multi-channel consistency ensures a reliable and professional user experience.
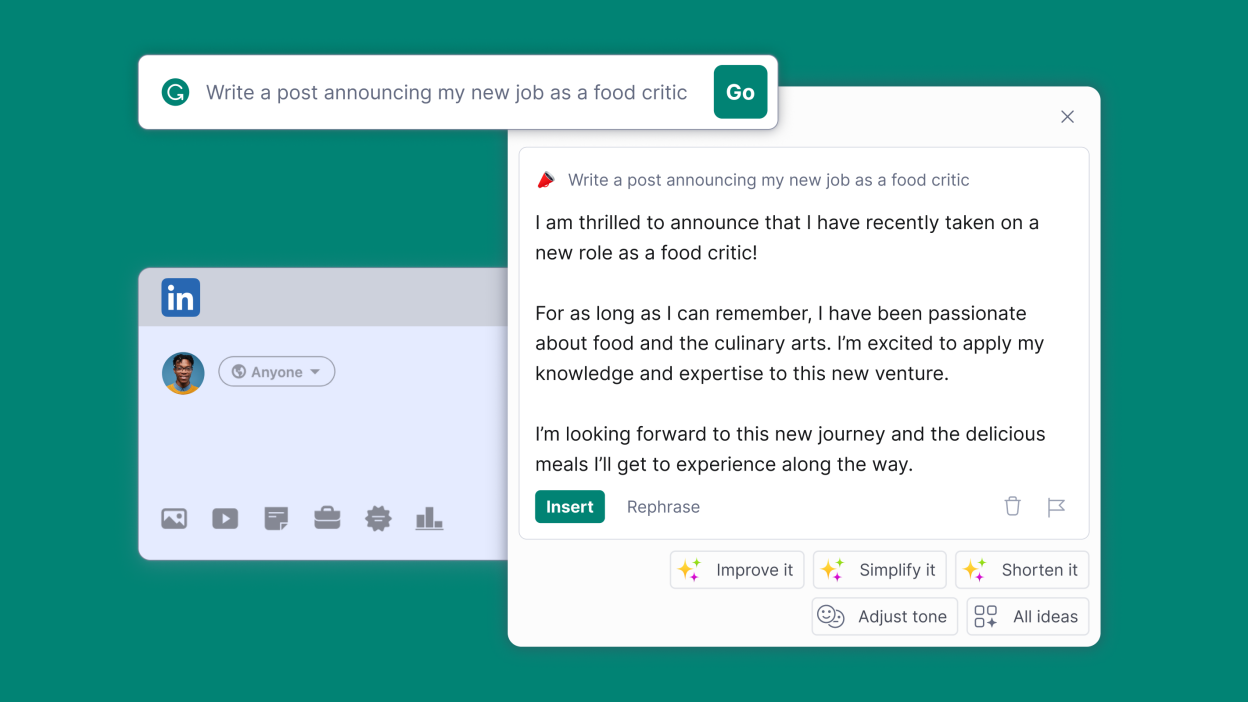
GrammarlyGO is an AI-powered chatbot integrated into Grammarly’s writing platform to help users draft, rewrite, and enhance text in real time. It supports everything from emails and reports to creative writing, making writing faster and more confident.
UX Highlights:
Context-Aware Suggestions: GrammarlyGO understands the user’s writing style, tone, and intent to provide tailored recommendations.
Conversational Interface: Users interact with the assistant through a chat-like interface, making the editing and drafting process feel natural and collaborative.
Multi-Use Scenarios: Whether you need help brainstorming ideas, improving clarity, or generating content from scratch, the assistant adapts to various writing needs.
Seamless Integration: Embedded within Grammarly’s existing tools, it enhances productivity without disrupting the workflow.
What You Can Learn:
Designing AI chatbots as creative partners that adapt to individual styles can make complex tasks like writing feel more approachable and enjoyable.
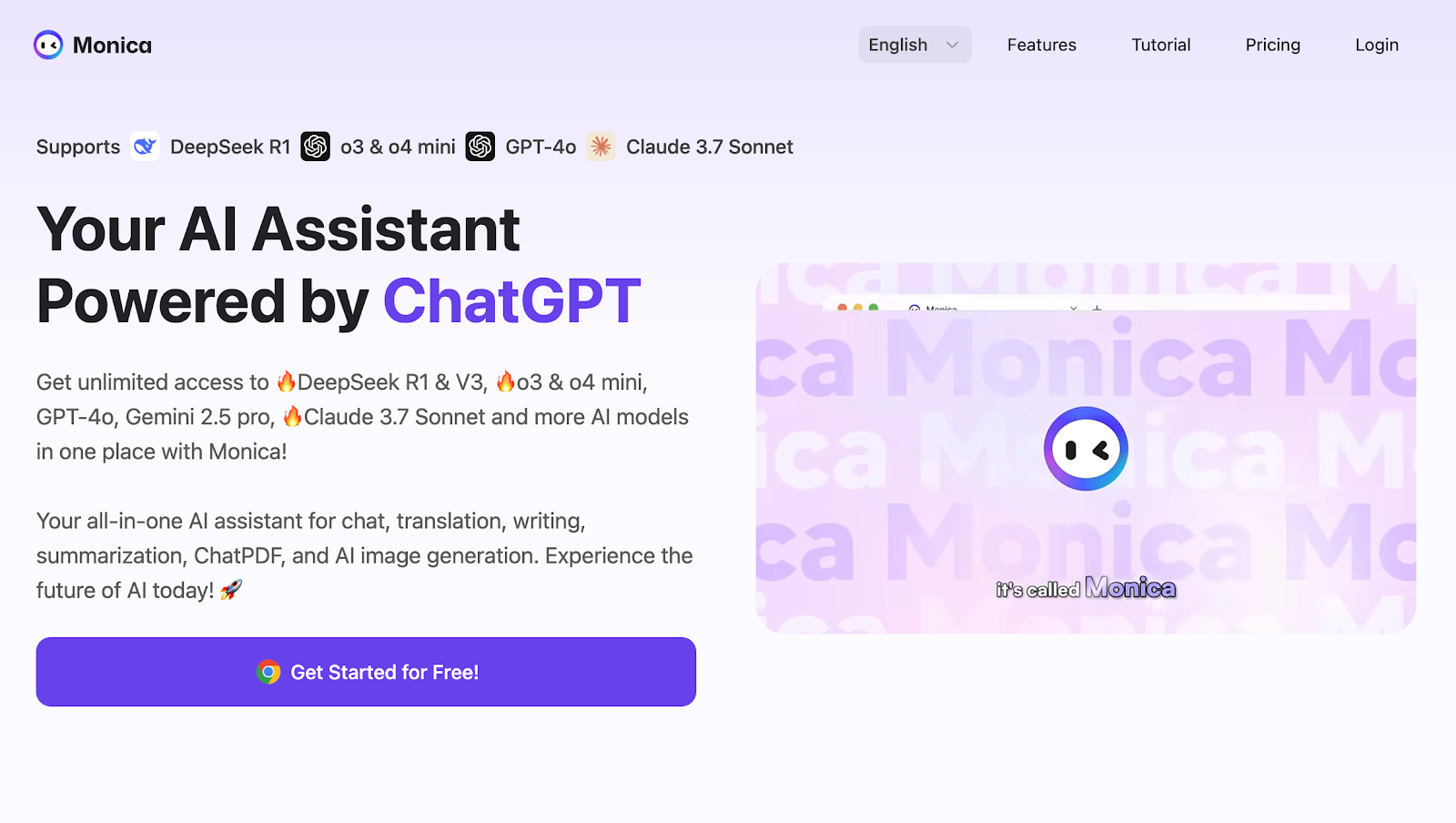
Monica is an advanced AI-powered assistant available as a browser extension and app that helps users with chatting, writing, summarizing, translating, and more—all from one unified platform. By integrating multiple cutting-edge AI models like GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.0, Monica offers versatile AI tools that boost productivity across devices.
UX Highlights:
Seamless Integration: Monica works directly within your browser or app, so you don’t need to switch contexts to use AI features.
Multi-Model Flexibility: Users can choose from various AI models tailored for different tasks, ensuring optimal results every time.
Cross-Platform Consistency: Available on desktop and mobile, Monica provides a smooth and unified experience regardless of device.
User-Friendly Interface: Its intuitive design allows easy access to tools like chat, writing templates, summarizers, translators, and AI art generators.
What You Can Learn:
Combining multiple advanced AI engines into a single, easy-to-access platform enhances creativity and efficiency, while cross-device support ensures users can stay productive anywhere.
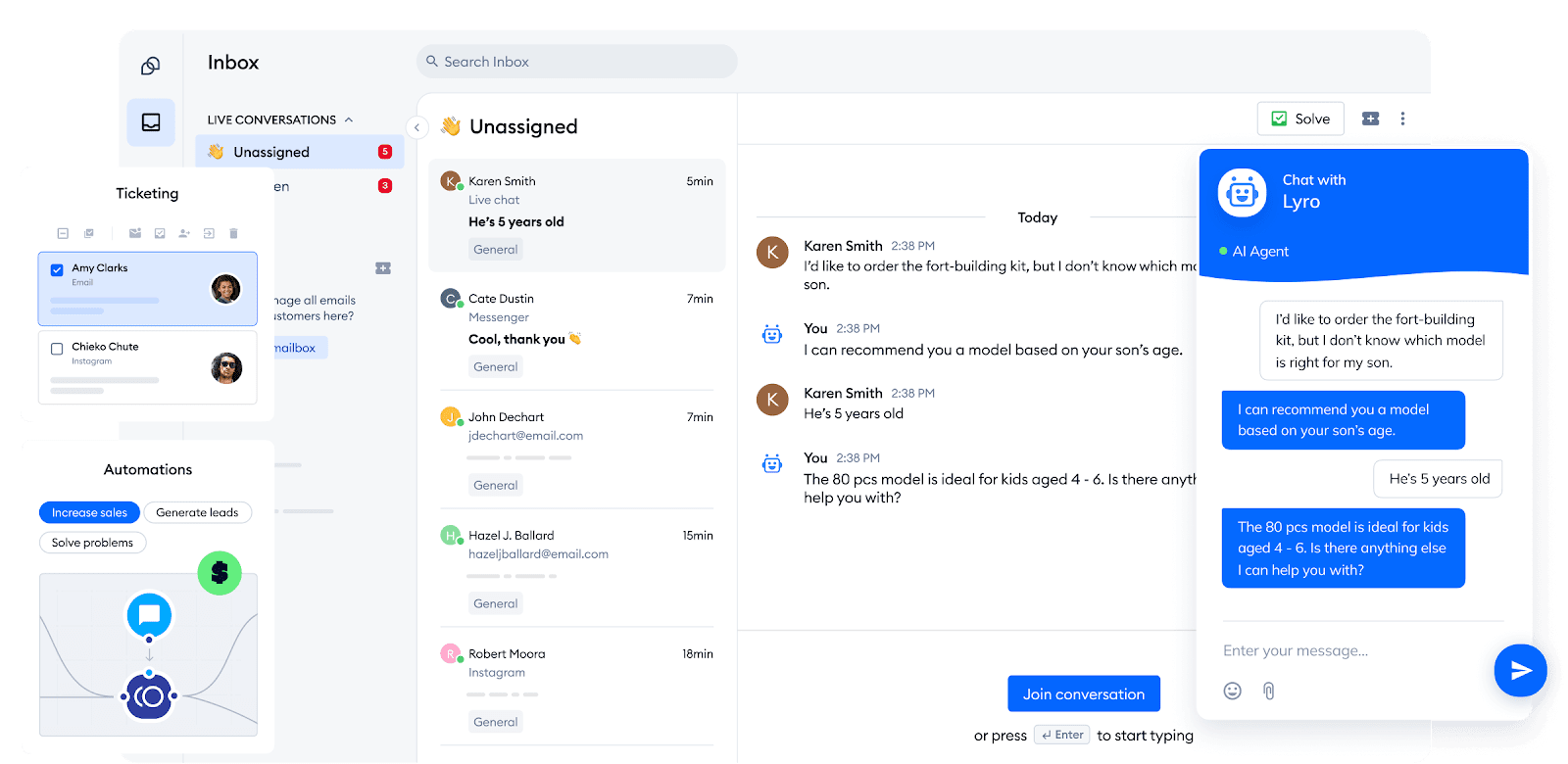
Tidio AI is an intelligent chatbot designed to enhance online store experiences—providing customers with real‑time assistance, personalized service, and automated support throughout their shopping journey.
UX Highlights:
Real-Time Intent Detection: Quickly recognizes user needs (e.g., product inquiries, order tracking) and delivers relevant responses without delays.
Proactive Engagement: Offers timely prompts like “Can I help you find something?” or “Looking for a discount?” to guide customer interaction and reduce decision fatigue.
Omnichannel Consistency: Available across web chat, email, and social media, ensuring a seamless brand experience across platforms.
Seamless CRM Integration: Links to dashboards, order history, and CRM tools, enabling personalized and informed conversations tailored to each shopper.
What You Can Learn:
Providing fast, context-aware support where customers already are—combined with proactive suggestions and seamless integration—can significantly enhance satisfaction, boost sales, and reduce cart abandonment.
18.YouChat – Conversational AI Search Assistant from You.com
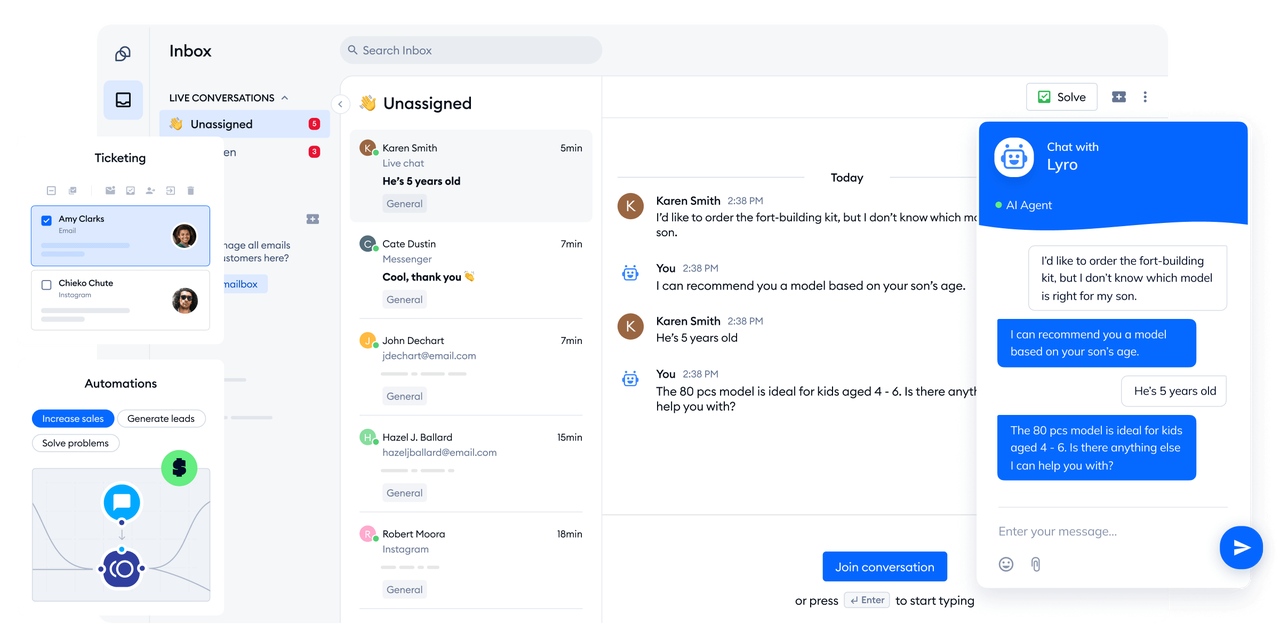
YouChat is an AI-powered chat assistant embedded directly within You.com’s search engine. It transforms traditional search into a conversational experience, allowing users to ask questions naturally and receive synthesized, context-aware answers—all while retaining source citations.
UX Highlights:
Conversational Search Interface: Users can ask follow-up questions without restating context, making exploration feel intuitive and chat-like rather than keyword-based ones.
Real-Time Information with Sources: Pulls up-to-date responses from the web and cites reference links directly in the chat, helping users verify and trust the content.
Multimodal Output: Supports text, charts, images, code snippets, and multimedia content inline—delivering richer, more useful responses than plain text alone.
Clean, Flexible UI & Modes: Adopts both horizontal and vertical scrolling; users can switch between AI Modes like Smart, Research, and Create for different tasks or content types.
Privacy-First Design: Offers private and personal modes to limit tracking and ads, appealing to users who prioritize control over their data.
What You Can Learn:
Combining chatbot UX with a search experience elevates usability—context-preserving dialogue, real-time results, and visual variety make complex information feel approachable and trustworthy.
Replika is an AI chatbot designed to serve as a virtual friend, offering emotional companionship through natural, open-ended conversations. With millions of users worldwide, it uses large language models to simulate human-like empathy, making users feel heard, understood, and supported.
UX Highlights:
Human-Like Personality: Replika’s conversational tone evolves based on how users interact, building a sense of emotional connection and personal growth.
Customizable Avatars: Users can customize their Replika’s name, appearance, and relationship type (friend, mentor, partner), personalizing the experience further.
Emotional Check-Ins: It regularly asks how you're feeling and responds appropriately, creating a safe space for reflection.
Gamified Growth: As conversations continue, the bot levels up, unlocking new skills and conversation topics that reward long-term engagement.
What You Can Learn:
Emotional intelligence and personalization can greatly increase retention and user satisfaction, especially in AI companions designed for daily interaction.

Kuki (formerly known as Mitsuku) is an award-winning chatbot designed primarily for entertainment. Built by Pandorabots, it focuses on general-purpose conversation, humor, and engaging interactions with a personality, winning multiple Loebner Prizes for “most human-like AI.”
UX Highlights:
Conversational Fun: Kuki engages users with jokes, games, and witty banter rather than task-oriented dialogue, making interactions light-hearted and engaging.
Cross-Platform Availability: Available across Messenger, Telegram, Kik, and its own web interface, making access easy across devices.
Avatar-Driven Interface: Kuki is often paired with an animated avatar that enhances personality and provides visual engagement.
Wide Knowledge Base: Trained on years of conversational data, it can handle diverse topics and open-ended questions.
What You Can Learn:
Personality and entertainment value can be just as important as utility in user engagement—especially in chatbots built for casual conversation or brand affinity.
Designing an effective AI chatbot is more than just implementing cutting-edge technology—it requires careful attention to user experience to ensure interactions feel natural, helpful, and engaging. Below are essential best practices grounded in UX principles to help you create chatbots that delight users and meet business goals.
Before building a chatbot, clearly identify the user problems it will solve and the business objectives it will support. This focus helps avoid unnecessary complexity and ensures your chatbot delivers real value.
Example: Customer support bots should prioritize fast, accurate answers and seamless escalation to humans.
Write chatbot dialogue in a tone and style that resonates with your target users. Use simple, clear language and avoid jargon.
Provide friendly, empathetic responses that reflect your brand voice.
Use positive, encouraging phrases to guide users.
Include confirmations and summaries to avoid misunderstandings.
Accommodate different user preferences by supporting text input, quick reply buttons, voice commands, and even emojis or GIFs where appropriate.
Quick reply buttons reduce typing effort and guide users toward valid options.
Voice input can improve accessibility and convenience, especially on mobile devices.
Design your chatbot to remember previous interactions and user preferences during a session to provide coherent and personalized responses.
Use session variables and user profiles to tailor dialogue.
Allow users to easily revisit or change earlier inputs.
Users should always know what the chatbot is doing or why it might have misunderstood them.
Display typing indicators or progress animations to manage user expectations.
When misunderstandings occur, offer helpful clarifications or alternative options rather than generic error messages.
Recognize the chatbot’s limitations and design smooth handoff processes to human agents when complex queries arise.
Notify users when a human agent will take over and transfer conversation history to avoid repetition.
Offer easy access to human support at any stage if desired.
Avoid overwhelming users with long paragraphs. Break information into digestible chunks, use bullet points or numbered steps, and leverage visual elements.
Use rich media like images, carousels, or buttons to enhance clarity and engagement.
Conduct usability testing to observe how users interact with your chatbot, identify pain points, and gather feedback for improvement.
Use A/B testing on dialogue variations to optimize engagement.
Monitor conversation analytics to understand drop-off points and frequently misunderstood intents.
Design chatbot interfaces to support diverse user needs, including screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and multi-language support.
Use plain language and avoid cultural references that may confuse international users.
Provide alternative interaction modes for users with disabilities.
Be transparent about data collection and usage. Implement secure data handling practices and allow users to opt out of data sharing.
Clearly communicate privacy policies within the chatbot interface.
Avoid requesting sensitive information unless absolutely necessary.
AI chatbots have become essential tools in modern UI/UX design, offering users faster support, personalized experiences, and streamlined interactions. By combining advanced AI technology with strong UX principles like clear communication, empathy, and accessibility, designers can create chatbots that truly enhance user satisfaction and business outcomes. This guide aims to help you design intelligent, user-friendly chatbots that fit seamlessly into your digital products and deliver real value.
 Mockplus RP
Mockplus RP
A free prototyping tool to create wireframes or interactive prototypes in minutes.
 Mockplus DT
Mockplus DT
A free UI design tool to design, animate, collaborate and handoff right in the browser.